- SPECIALIST ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON | MELBOURNE, VIC | ALBURY, NSW | MORNINGTON, VIC |
- 03 9421 6133
- Melbourne & Mornington VIC |
- Albury, NSW
Chronic knee pain refers to ongoing or recurring pain in the knee that lasts longer than 3 months. It may develop gradually or result from an injury that fails to heal properly. Unlike acute pain, which often improves with rest and time, chronic knee pain tends to persist, impact daily activities, and may signal an underlying joint or soft tissue problem that requires medical attention.
Chronic knee pain is a common issue affecting people of all ages, from active individuals with overuse injuries to older adults experiencing degenerative joint conditions. If left unaddressed, it can lead to reduced mobility, muscle weakness, and long-term functional limitations.
This page provides a comprehensive overview of what causes chronic knee pain, how it is diagnosed, and what treatment options may help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
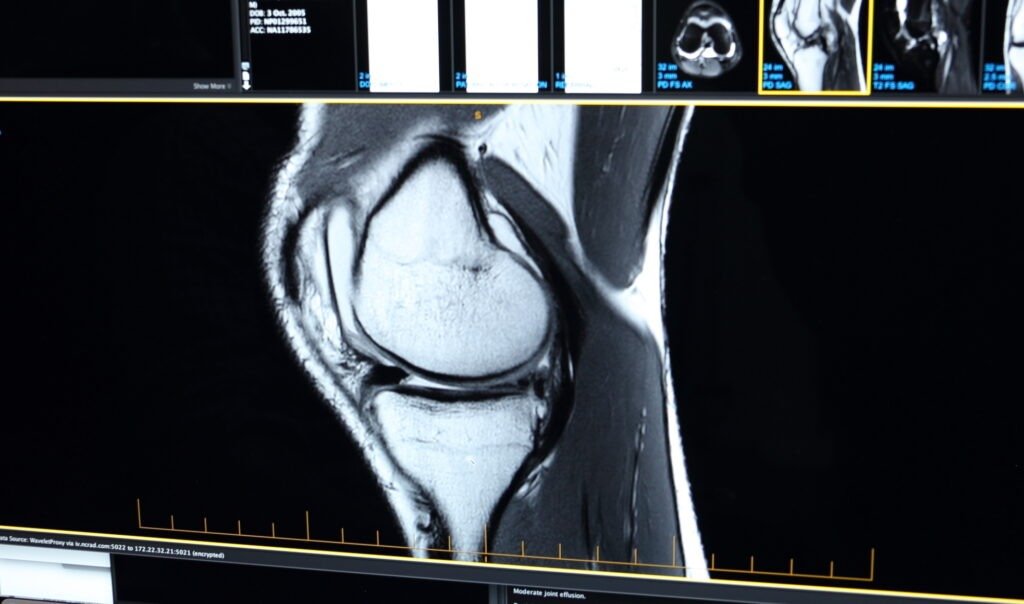
Dr Jason Hockings will conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of your symptoms. This typically includes:
Accurate diagnosis is key to creating a targeted treatment plan and preventing further joint damage.

If you’re experiencing ongoing pain, stiffness, or reduced movement that is affecting your daily activities or quality of life, a thorough orthopaedic assessment can help determine the cause and guide the most appropriate treatment options for your situation.