- SPECIALIST ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON | MELBOURNE, VIC | ALBURY, NSW | MORNINGTON, VIC |
- 03 9421 6133
- Melbourne & Mornington VIC |
- Albury, NSW
Avascular necrosis (AVN), also known as osteonecrosis, is a serious condition that occurs when the blood supply to a section of bone is disrupted. In the hip, this typically affects the femoral head, the ball-shaped part of the thigh bone that fits into the hip socket. Without adequate blood flow, the bone tissue begins to die, which can cause the femoral head to weaken, flatten, and eventually collapse.
AVN can develop gradually or progress rapidly, and often leads to hip pain, stiffness, and difficulty with walking or bearing weight. Over time, it may result in advanced arthritis of the hip joint.
A range of factors may contribute to AVN, including previous trauma (such as a hip fracture or dislocation), long-term use of corticosteroids, excessive alcohol intake, or certain medical conditions. However, in some cases, the cause may be unknown (idiopathic).
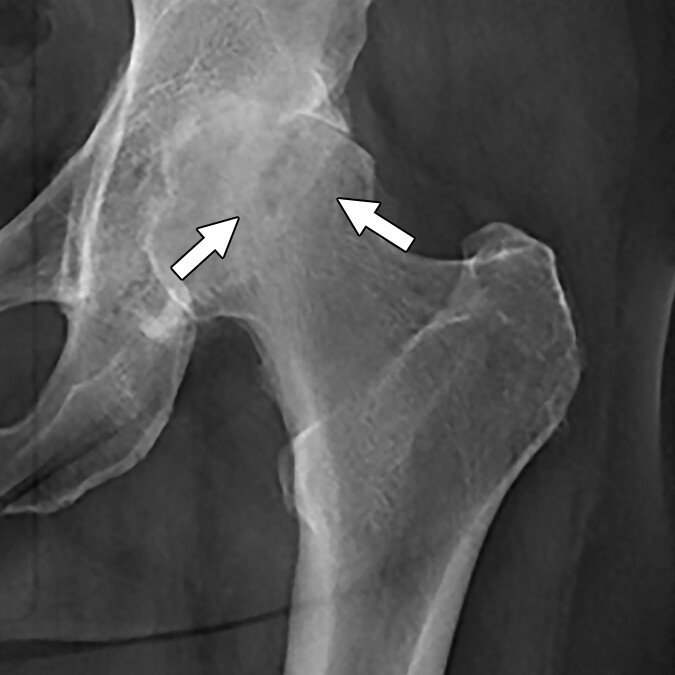
Early diagnosis is key, as some cases may be managed with non-surgical treatment if caught in the early stages. For advanced or progressive cases, surgery including total hip replacement may be recommended to restore function and relieve pain.
This page explains the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for AVN of the hip to help you better understand your condition and the pathways available for care.
Avascular necrosis (AVN), also known as osteonecrosis, is a condition that occurs when the blood supply to the femoral head (the ball of the hip joint) becomes disrupted. Without adequate blood flow, the bone tissue begins to die, leading to the collapse of the femoral head, joint deterioration, and eventually, arthritis. The hip is the most commonly affected joint in AVN, although other joints such as the shoulder or knee may also be involved.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important, as progression of the disease can lead to permanent damage requiring joint replacement surgery.

Avascular necrosis can result from a number of underlying causes that reduce blood flow to the femoral head. These may include:
In some cases, no clear cause can be identified — this is referred to as idiopathic AVN.
AVN may affect one or both hips. When both sides are involved, this is referred to as bilateral AVN.


If you’re experiencing ongoing pain, stiffness, or reduced movement that is affecting your daily activities or quality of life, a thorough orthopaedic assessment can help determine the cause and guide the most appropriate treatment options for your situation.